Introduction
Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) provides a powerful way to expose Oracle databases via REST, what if you could extend this capability to databases like DB/2, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server—without installing ORDS on each database? In summary, your applications can interact with multiple databases, because a universal RESTful interface can streamline access and reduce development complexity.
As an extensible product where you can develop your own plugins, you can code your own ORDS JDBC AutoREST Plugin. To learn more about plugins in ORDS see: Crafting your ORDS plugin the Maven way
What is the ORDS JDBC AutoREST Plugin?
The ORDS JDBC AutoREST Plugin is a custom plugin for Oracle REST Data Services that enables RESTful access to a variety of relational databases. Using standard JDBC, it acts as a bridge between ORDS and databases beyond Oracle, providing a unified API layer.
Key Features
- Multi-Database Support: Works with DB/2, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
- Standard JDBC: Uses JDBC drivers to communicate with target databases.
- No ORDS Installation Required: The target database does not need an ORDS installation.
- RESTful Interface: Automatically generates REST endpoints for CRUD operations.
- API Driven: The service definition metadata is in an OpenAPIV3 document which is reloaded every 5 minutes. Changes are picked up without a restart.
How It Works
Architecture Overview
The plugin integrates with ORDS and utilizes JDBC to interact with databases. ORDS remains the entry point, processing RESTful requests and translating them into SQL queries executed via JDBC connections.
- A client sends a REST request to ORDS.
- ORDS uses the basic authentication credentials to make a JDBC connection to the target database.
- The ORDS JDBC AutoREST Plugin reads the API document that describes the database objects and services. It then generates the SQL statement and executes it over JDBC.
- The database processes the request and returns results.
- ORDS formats and sends back the response.
Subtle difference from ORDS AutoREST:
- No installation required in the database
- No HATEOS links generated
- Only basic authentication
Of course, since you are building your own custom plugin, you can code any additional functionality you want.
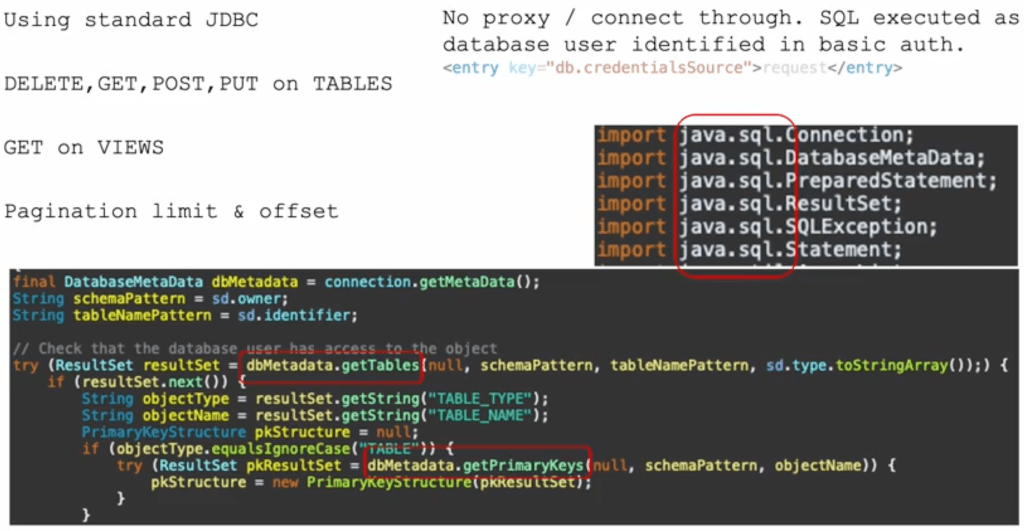
Example Usage
Once configured, the plugin enables RESTful endpoints that map to database tables and views. For instance, a request to:
GET /autorest/employees/
Could return JSON data from an employees table, regardless of whether the underlying database is Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc. Note that a HTTP request will require basic authentication with credentials for a database user and that user must have access to the underlying data.
Setting Up the Plugin
Prerequisites
- Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) installed and running.
- JDBC drivers for the target databases.
Installation Steps
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/pobalopalous/ords-jdbc-autorest.git - Build the plugin and deploy it into your ORDS instance.
- Configure database connections using JDBC connection strings.
- Update the API document for your database to target tables or views.
Using x-autorest extension
An extension called x-autorest is used in the API document to define what tables and views are to be available, as well as what operations ( DELETE, GET, PUT, POST ) are permitted. Note that this requires that tables are defined with a primary key.


A description of the x-autorest extension.
x-autorest:
owner: DB2INST1 // Database user that owns the object
identifier: INVENTORY // The database object
type: table // The type of object table or view
Benefits & Use Cases
Why Use This Plugin?
- Simplified API Development: Unified RESTful API for multiple databases.
- Reduced Overhead: No need to install ORDS on every database.
- Flexible Database Integration: Easily switch between databases without major application changes.
Ideal Use Cases
- Multi-database applications needing a standardized REST API.
- Data migration projects requiring uniform RESTful access.
- Reporting and analytics tools aggregating data from multiple sources.
Conclusion
The ORDS JDBC AutoREST Plugin provides a powerful way to extend RESTful database access beyond Oracle to DB/2, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. With minimal setup and configuration, developers can use ORDS to expose database resources through a standard REST API, ensuring reliability without needing to install ORDS on each target database.
Explore the source code and start using it today: GitHub Repository.